What is PRDP?
The Philippine Rural Development Project is a national project under the Department of Agriculture (DA) that aims to establish a modern, value-chain oriented, and climate resilient agriculture and fisheries sector. It is jointly funded by the World Bank, the National Government and the Local Government Units (LGUs).
In partnership with LGUs and private sector, PRDP shall provide key infrastructure, facilities, technology and information to raise incomes, productivity and competitiveness in targeted areas.
Likewise, it aims to strengthen good governance, transparency and accountability mechanisms at all stages of the project cycle. It also intends to operationalize a local level convergence platform among relevant national line agencies and other stakeholders (private sector, civil society, producers, and academe) to synergize projects and programs that benefit the greater segment of the farmers and fishers towards attaining inclusive growth.
Who are the target beneficiaries of the Project?
PRDP will support smallholder farmers and fishers to primarily increase their marketable surpluses and their access to markets.
Under the PRDP’s Enterprise Development Component (I-REAP), the small-scale agricultural, livestock and fishery producers, processors, and traders who are identified in the priority value chains of the products or commodities of the region/province are the target proponent groups.
They have to be an existing organized and duly registered farmer associations and cooperatives that are being strengthened or aggregated into clusters to directly benefit from the Project through technical services, trainings, market linkages, and financial assistance.
Infrastructure Development Component (I-BUILD) will benefit producers, traders and rural population in general through construction of farm-to-market roads, bridges, communal irrigation systems, potable water systems, and other infrastructures like production, processing, marketing, and postharvest facilities that support development and linking of priority commodity value chains in project areas.
Moreover, assistance to women will be given focus through enterprise development and business aspects of farming, post-harvest handling and processing that are typically managed by women in the country.
How is the cost financing among the World Bank (WB), National Government (NG) and Local Government Unit (LGU) divided for PRDP sub-projects?
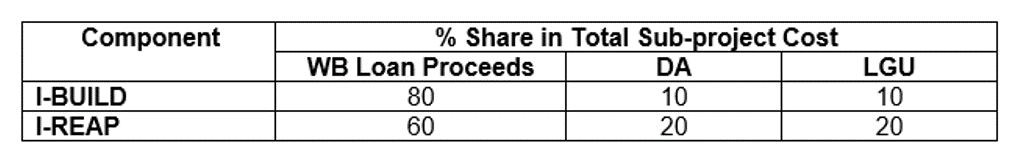
Note: For subprojects under Enterprise Development, the Proponent Group will provide equity of at least 20% to the total incremental enterprise cost
What are the eligible sub-projects under PRDP and the corresponding standard specifications and unit cost?
Under the Infrastructure Development Component, the following are the eligible sub-projects:
1. Farm-to-Market Roads (FMRs)
2. Bridges
3. Communal Irrigation System (CIS)
4. Potable Water System
5. Other types of rural infrastructures needed in the value chains to enhance the productivity and give value-added qualities to products in the agri-fishery industries e.g.(i) production facilities, post-harvest facilities, marketing facilities, fish landings, fish sanctuaries/marine protected areas, tram lines, green houses, solar driers, watch towers, nursery watch towers and slope stabilization works; and (ii) municipal/provincial roads, cold storage facilities and trading posts but need prior concurrence from NPCO and the World Bank.
PRDP Process Flow
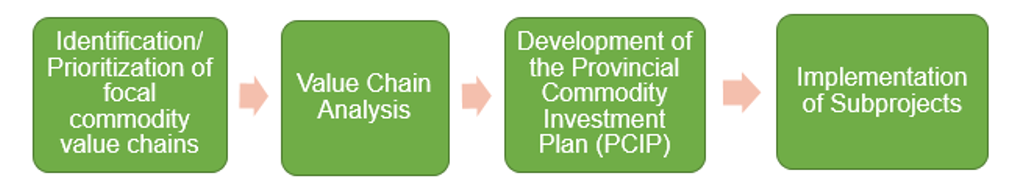
General Process Flow for Subprojects
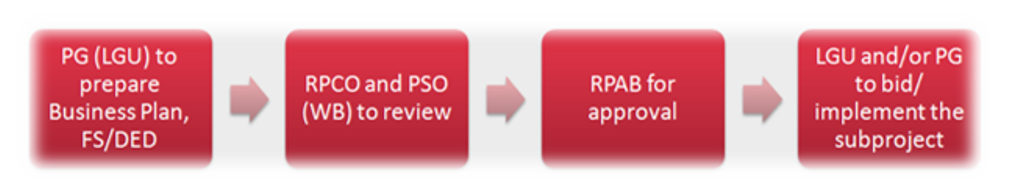
Provincial Commodity Investment Plan (PCIP)
The PCIP contains the various enterprise development, infrastructure and implementation support sub-projects and investment opportunities for priority commodities in the province. The PCIP for calamansi was formulated in 2014. It was updated in 2017 to include the second priority commodity – virgin coconut oil and in 2019 to include the third priority commodity – banana. In 2021, the updated PCIP 2022-2024 includes proposed interventions for the swine industry.
PRDP-Funded Projects
1. Concreting of Bagong Silang-Macatoc Farm-to-Market Road in Victoria (2.7882 kilometers)
2. Concreting of Dulangan I-II Farm-to-Market Road in Baco (5.3077 kilometers)
3. Construction of Oriental Mindoro Calamansi Trading Center in Bayanan II, Calapan City
4. Construction of Calamansi Buying Station in Victoria
5. Construction of Oriental Mindoro Calamansi Processing Center and Marketing in Matulatula, Pola
